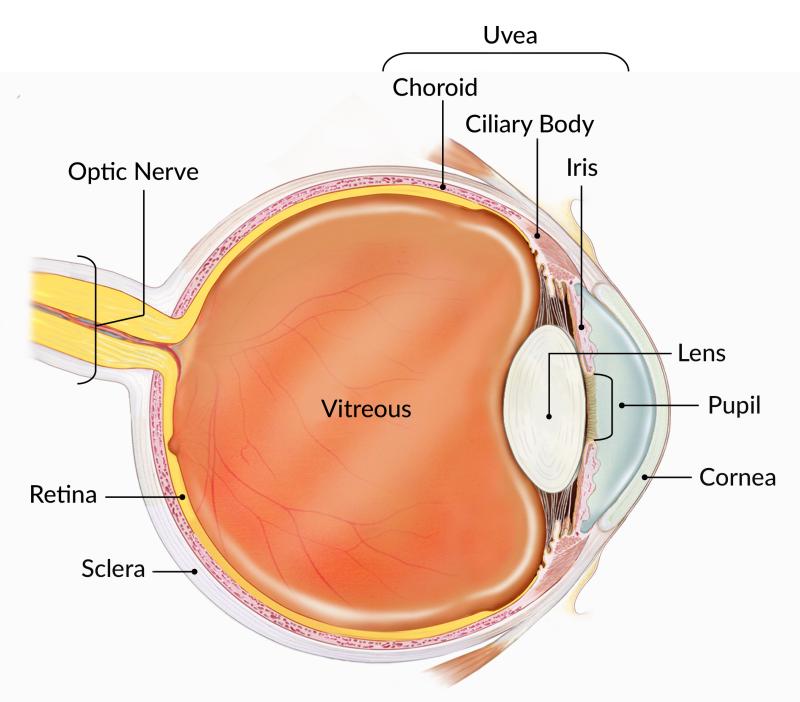
All the different parts of your eyes work together to help you see.
First, light passes through the cornea (the clear front layer of the eye). The cornea is shaped like a dome and bends light to help the eye focus.
Some of this light enters the eye through an opening called the pupil (PYOO-pul). The iris (the colored part of the eye) controls how much light the pupil lets in.
Next, light passes through the lens (a clear inner part of the eye). The lens works together with the cornea to focus light correctly on the retina.
When light hits the retina (a light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eye), special cells called photoreceptors turn the light into electrical signals.
These electrical signals travel from the retina through the optic nerve to the brain. Then the brain turns the signals into the images you see.
Your eyes also need tears to work correctly.