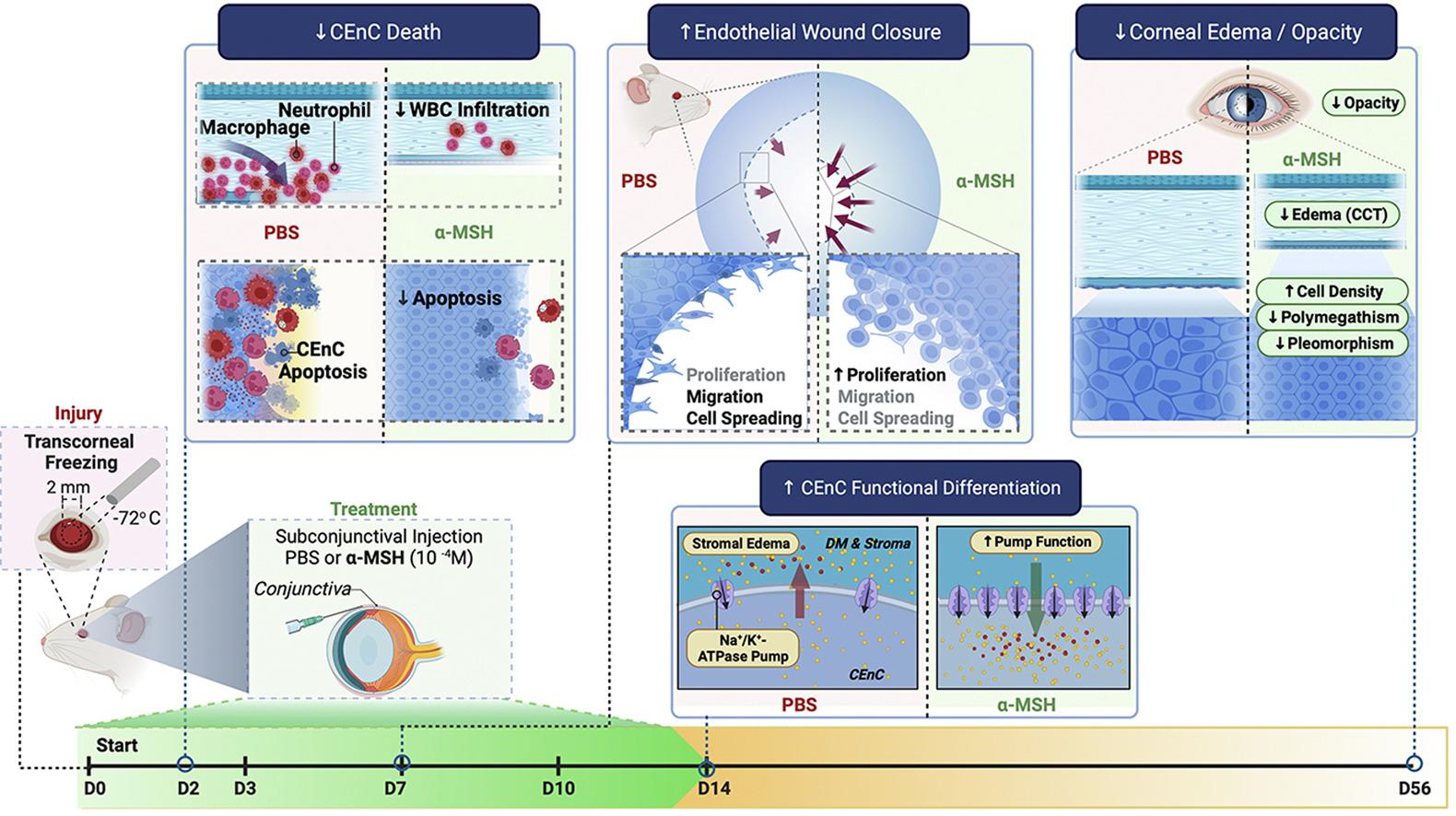
Researchers at Harvard Medical School have demonstrated the potent therapeutic effects of administration of the neuropeptide α-melanocyte–stimulating hormone (α-MSH) through melanocortin receptor agonism, providing compelling evidence for the therapeutic potential of this pathway for a wide array of eye disorders. CEnC, corneal endothelial cells; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline. Image credit: The American Journal of Pathology
Findings from a pioneering study in The American Journal of Pathology reveal that administration of the neuropeptide α-melanocyte–stimulating hormone (α-MSH) promotes corneal healing and restores normal eye function to an otherwise degenerating and diseased cornea by providing protection against cell death and promoting cell regeneration.
This study examined the effect of local administration of α-MSH on persistent corneal edema and endothelial regeneration in an established model of injury-induced endothelial decompensation. The results show the impressive therapeutic potential of promoting the melanocortin pathway using α-MSH, thus opening new avenues of therapy.